The architecture of VTS test framework integrates with its cloud-based test serving service. A VTS host controller runs on a host machine and controls a test harness (for example, Tradefed) instance as shown below:
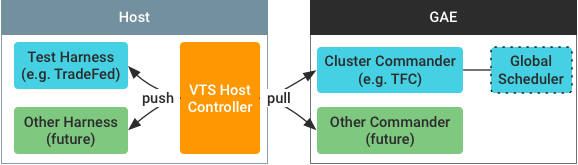
Figure 1. VTS host controller architecture.
The controller pulls commands from a cluster commander running as a Google App Engine (GAE) instance, then relays commands and responses between its cluster commander and the test harness instance.
This architecture includes the following advantages:
- Because it's decoupled from any test harness instance, it can control different types of test harnesses and is more robust. The alternative design (embedding the host control logic in a test harness) does not block errors from propagating.
- Because it uses a pull-based command-and-control (C&C) model, it can work with different types of cloud-side cluster commanders as well as hosts that exist behind a firewall (for ingress connections). The alternative design (push-based C&C model) might not allow a cloud commander to access host controller instances that exist on host computers in a private network.
